IP type of service field (RFC1349) = 00100000 (32)
Precedence (priority) = 001 (priority)
Delay = 0 (normal delay)
Throughput = 0 (normal throughput)
Reliability = 0 (normal reliability)
Cost = 0 (normal cost)
Check bit = 0 (correct, 8th checking bit must be zero)
DSCP (DiffServ) = CS1 001000 (8) - class 1 (RFC 2474). Similar forwarding behavior to the ToS Precedence field.
on puc veure que basicament he de canviar el mtu, donat que valors més petits 1500 semblan optimitzats per entorns adsl. i RWIN posar-ho a 1022208
finalment he fet també una prova amb el següent link
http://www.dslreports.com/tweaks
on hi ha un petit applet per fer una altra prova de velocitat

passats 20 segons del test

on podeu veure que hi ha un recomendació del paràmetre a modificar.
Change MTU to 1500 (FAQ #652, #695)
 Vista has no tunable TCP settings Vista has no tunable TCP settings
 Read the tweak FAQ Read the tweak FAQ
(he fet la modificació pero no trobo millora destacable.....)
per finalitzar, col·loco enllaç de modificacions d'aquest paràmetres en windows seven....
http://www.speedguide.net/articles/windows-7-vista-2008-tweaks-2574
Windows 7, Vista, 2008 Tweaks
Tweaking Windows 7 / Vista TCP/IP settings for broadband internet connections
2008.04.24 10:40 by Philip
Keywords: patch, Nagle, QoS, SynAttackProtect, DNS, DefaultTTL, NetDMA, TCP 1323 Options, MTU, auto-tunning, Compound TCP, Chimney Offload, CTCP, TCP Window, Registry, TCP/IP, tweak, Vista, Windows 7
Windows Vista introduces a number of new features to the TCP/IP stack, including CTCP, and TCP Window Auto-Tuning. This new implementation works much better by default than previous Windows versions with broadband internet connections, and is able to adjust the RWIN value on the fly, depending on the BDP
(bandwidth-delay product). This, however, introduces some problems with
older routers and restricts the user from tweaking some of the TCP/IP parameters. Still, there is always some room for improvement, and this article explains the known tweakable TCP/IP parameters.
To
enter some of the commands below, you will need to run "elevated"
command prompt. To do so, click the Start icon > Run > type: cmd ,
then click CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. Alternatively, you can navigate to Start
> All Programs > Accessories > right-click Command Prompt and
choose "Run as Administrator".
Check the TCP/IP state
To check the current status of the Vista TCP/IP tweakable parameters, in elevated command prompt type the following command:
netsh int tcp show global
You will be presented with something like the following:
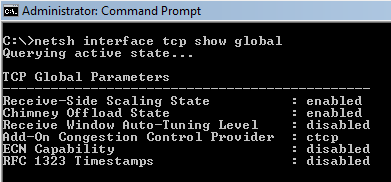
The
settings, as well as their default and recommended state are explained
below. The two most important tweakable parameters are "Auto-Tuning
Level" and "Congestion Control Provider".
When checking the TCP
state with the "netsh int tcp show global" command, it is also possible
to see the following message below all those parameters:
**
The above autotuninglevel setting is the result of Windows Scaling
heuristics overriding any local/policy configuration on at least one
profile.
It is displayed when the "Receive Window
Auto-Tuning Level" is not explicitly set, or if the system deemed it
necessary to make a change because of user prompted "repairing" of your
network connection, for example.
Disable Windows Scaling heuristics
Windows
Vista/7 has the ability to automatically change its own TCP Window
auto-tuning behavior to a more conservative state regardless of any user
settings. It is possible for Windows to override the
autotuninlevel even after an user sets their custom TCP auto-tuning
level. When that behavior occurs, the "netsh int tcp show global"
command displays the following message:
** The above autotuninglevel setting is the result of Windows Scaling heuristics
overriding any local/policy configuration on at least one profile.
To prevent that behavior and enforce any user-set TCP Window auto-tunning level, you should execute the following command:
netsh int tcp set heuristics disabled
possible settings are: disabled,enabled,default (sets to the Windows default state)
recommended: disabled (to retain user-set auto-tuning level)
Note
this should be executed in elevated command prompt (with admin
priviledges) before setting the autotuninlevel in next section. If the
command is accepted by the OS you will see an "Ok." on a new line.
The corresponding Registry value (not necessary to edit if setting via netsh) is located in:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters
EnableWsd=0 (default: 1, recommended: 0)
TCP Auto-Tuning
To turn off the default RWIN auto tuning behavior, (in elevated command prompt) type:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled
The default auto-tuning level is "normal", and the possible settings for the above command are:
disabled: uses a fixed value for the tcp receive window. Limits it to 64KB (limited at 65535).
highlyrestricted: allows the receive window to grow beyond its default value, very conservatively
restricted: somewhat restricted growth of the tcp receive window beyond its default value
normal: default value, allows the receive window to grow to accommodate most conditions
experimental:
allows the receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios (not
recommended, it can degrade performance in common scenarios, only
intended for research purposes. It enables RWIN values of over 16 MB)
Our recommendation: normal (unless you're experiencing problems).
If you're experiencing problems with your NAT router or SPI firewall, try the "restricted", "highlyrestricted", or even "disabled" state.
Notes:
- Reportedly, some older residential NAT routers with a SPI firewall may have problems with enabled tcp auto-tuning in it's "normal" state, resulting in slow speeds, packet loss, reduced network performance in general.
- auto-tuning also causes problems with really old routers that do not support TCP Windows scaling. See MSKB 935400
- netsh set commands take effect immediately after executing, there is no need to reboot.
- sometimes when using "normal" mode and long lasting connections (p2p
software / torrents), tcp windows can get very large and consume too
much resources, if you're experiencing problems try a more conservative
(restricted) setting.
If you're experiencing problems with Auto-Tuning, see also:
MSKB 835400 - email issues
MSKB 934430 - network connectivity behind firewall problems
MSKB 940646 - 3G WWAN throughput issues
MSKB 929868 - web browsing issues
MSKB 932170 - slow network file transfer
Compound TCP - Improve throughputAdd-On Congestion Control Provider
The
traditional slow-start and congestion avoidance algorithms in TCP help
avoid network congestion by gradually increasing the TCP window at the
beginning of transfers until the TCP Receive Window boundary is reached,
or packet loss occurs. For broadband internet connections that combine high TCP Window with higher latency (high BDP), these algorithms do not increase the TCP windows fast enough to fully utilize the bandwidth of the connection.
Compound TCP (CTCP) is a newer method, available in Vista and Server 2008 (there is also a hotfix available for XP x64 and 2003 Server - MSKB 949316). CTCP increases the TCP send window more aggressively for broadband connections (with large RWIN and BDP). CTCP attempts to maximize throughput by monitoring delay variations and packet loss. It also ensures that its behavior does not impact other TCP connections negatively.
By default, Vista and Windows 7 have CTCP turned off, it is only on by default under Server 2008. Turning this option on can significantly increase throughput and packet loss recovery.
To enable CTCP, in elevated command prompt type:
netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=ctcp
To disable CTCP:
netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=none
Possible options are: ctcp, none, default (restores the system default value).
Recommended setting: ctcp
It is better to use this newer generation CTCP congestion control algorithm for most broadband connections, we highly recommend it being turned on.
ECN Capability
ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification, RFC
3168) is a mechanism that provides routers with an alternate method of
communicating network congestion. It is aimed to decrease
retransmissions. In essence, ECN assumes that the cause of any packet loss is router
congestion. It allows routers experiencing congestion to mark
packets and allow clients to automatically lower their transfer rate to
prevent further packet loss. Traditionally, TCP/IP networks signal congestion by dropping packets. When ECN is successfully negotiated, an ECN-aware router may set a bit in the IP header (in the DiffServ field) instead of dropping a packet in order to signal congestion. The receiver echoes the congestion indication to the sender, which must react as though a packet drop were detected.
ECN is disabled by default in Vista and other modern TCP/IP
implementations, as it is possible that it may cause problems with some
outdated routers that drop packets with the ECN bit set, rather than
ignoring the bit. To check whether your router supports ECN, you can use the Microsoft Internet Connectivity Evaluation Tool. The results will be displayed under "Traffic Congestion Test".
To change ECN, in elevated command prompt type:
netsh int tcp set global ecncapability=default
Possible settings are: enabled, disabled, default (restores the state to the system default).
The default state is: disabled
Recommendation:
enabled (only for short-lived, interactive connections and HTTP
requests with routers that support it, in the presense of
congestion/packet loss), disabled otherwise (for pure bulk throughput with large TCP Window, no regular congestion/packet loss, or outdated routers without ECN support).
Notes: ECN is only effective in combination with AQM (Active Queue Management) router policy. It has more noticeable effect on performance with interactive connections and HTTP requests, in the presense of router congestion/packet loss. Its effect on bulk throughput with large TCP Window are less clear.
Currently, we do not recommend enabling this setting, as reportedly it has negative impact on throughput
with some residential US ISPs. EA multiplayer games that require a
profile logon do not support ECN as well (you will not be able to
logon).
More information on ECN: Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) for TCP/IP
RSS - Receive-side Scaling
The receive-side scaling setting enables parallelized processing of received packets on multiple processors, while avoiding packet reordering. It avoids packet
reordering y separating packets into "flows", and using a single
processor for processing all the packets for a given flow. Packets are
separated into flows by computing a hash value based on specific fields
in each packet,
and the resulting hash values are used to select a processor for
processing the flow. This approach ensures that all packets belonging to
a given TCP connection will be queued to the same processor, in the
same order that they were received by the network adapter.
To set RSS:
netsh int tcp set global rss=enabled
Possible rss settings are: disabled, enabled, default (restores rss state to the system default).
Default state is: enabled
Recommended: enabled (if you have 2 or more processor cores and a NIC that can handle RSS)
In Windows Server 2008, the system default is for RSS to be enabled and to use a maximum of four CPUs. While this is usually enough, administrators can adjust the maximum number of RSS processors by setting the MaxNumRssCpus registry value in HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NDIS\Parameters.
The value type is DWORD, and if not present, the default value of four
processors is assumed (do not use value greater than 32).
See also: Receive-Side Scaling Enhancements in Windows Seerver 2008
TCP Chimney Offload
TCP
chimney offload enables Windows to offload all TCP processing for a
connection to a network adapter. Offloads are initiated on a
per-connection basis. Compared to task offload, TCP chimney offload
further reduces networking-related CPU overhead, enabling better overall
system performance by freeing up CPU time for other tasks.
To set TCP Chimney Offload:
netsh int tcp set global chimney=enabled
Default state: disabled (under Vista), automatic (under Windows 7 and 2008 Server)
Recommended: enabled
The possible states are disabled, enabled, default (Vista), automatic (only Windows 7 and 2008 Server) as follows:
automatic
- This default setting is only available under Windows 7 and 2008
Server, it is not available udner Vista. It offloads if the connection
is 10 GbE, has a RTT < 20ms, and the connection has exchanged at least 130KB of data. The device driver must also have TCP Chimney enabled.
default
- this setting restores chimney offload to the system default. Setting
this "default" state under Windows 7 and 2008 Server is possible, but it
sets the system to the "automatic" mode described above.
disabled - this setting is maually configured as disabled.
enabled - this setting is manually configured as enabled.
Notes:
Under Windows
7 and Server 2008 the "default" and the additional
"automatic" parameter set the system to the same "automatic" state.
For Chimney Offload to work, it needs to be enabled in both the OS and NIC. To enable the "TCP Offloading" setting in your NIC,
navigate to the Device Manager, under Network Adapters, in the Advanced
tab, and check "Enabled" in the box next to the TCP offload entry.
Direct Cache Access (DCA)
Windows
7 and 2008 Server (but not Vista) add NETDMA 2.0 Direct cache
access support. Direct Cache Access (DCA) allows a capable I/O device,
such as a network controller, to deliver data directly into a CPU cache.
The objective of DCA is to reduce memory latency and the memory bandwidth requirement in high bandwidth (Gigabit) environments. DCA requires support from the I/O device, system chipset, and CPUs.
To enable DCA:
netsh int tcp set global dca=enabled
Available states are: enabled, disabled.
Default state: disabled
Recommended: enabled (provided the CPU/Chipset/NIC support it)
It is also possible to enable this setting by editing the Windows Registry instead of using netsh as follows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\ParametersEnableDCA=1 (DWORD, entry does not exist by default. Set to 1 to enable, 0 to disable)
Setting MTU
It is sometimes useful to view and set the MTU value for a specific network interface manually. To view a list of active network interfaces and their MTU values in Vista using netsh, open command prompt as administrator and execute the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterface
You will be presented with a list of interfaces, and their respective MTU values as follows:
To change the MTU value of a specific network card, type the following in command prompt:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface "network interface name" mtu=#### store=persistent
Where
"network interface name" is your specific network adapter name as
obtained above (or viewable under Network adapters), and mtu=#### is the
desired MTU value.
For example, if the name of your network card is "Wireless Network Connection" and you'd like to set its MTU to 1500, you'd have to type:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface "Wireless Network Connection" mtu=1500 store=persistent
Note: The maximum MTU value is usually 1500, and up to 1492 for PPPoE connections.
Manually tuning Registry Parameters
Many of the registry keys tuning TCP/IP
parameters from previous Windows versions no longer work in Vista and
Server 2008. Below is a list of the few we've confirmed to still work,
as well as some new additions. Note that for changes to these settings
to take effect the computer needs to be rebooted. As always, a registry
backup is recommended if making any changes, and some proficiency in
using regedit is required.
In regedit (Start icon > Run > type: regedit while logged in as administrator), you can navigate and edit the following keys.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) - the maximum packet size.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\{...}\
MTU=1500 (DWORD, entry does not exist by default)
The
{....} part of the above path is the unique identifier of your network
adapter. You can recognize the correct adapter by looking at it's IP address, if obtaining IP automatically labeled by: DhcpIPAddress=192.168.x.x text value, for example.
We recommend leaving this at default, unless you want to lower it. Vista uses the largest possible packet size for the underlying network by default.
Note: In some test environments, the correct MTU entry may be offset by 8. The 8 offset seems to coincide with the size of the PPPoE overhead. Check the result with the TCP Analyzer.
SMB Large MTU (SMB 2, CIFS network shares)
SMB 2 implementation in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 allows for using a large MTU value for very high speed/low latency Gigabit networks by enabling a new registry parameter, as follows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
DisableLargeMtu=0 (DWORD, default: 1, to enable Large MTUs: 0)
Note that client workstations may have to enable lare SMB MTU in this hive instead:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters
DisableLargeMtu=0
Note: This setting should only be applicable to SMB2 shares
TCP 1323 Options
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
Tcp1323Opts=1
(DWORD, entry created automatically by Windows when you run the
"netsh int tcp set global autotuninglvl=..." command, set to 0 by
default).
Setting this seems to have no effect, since auto-tuning
uses the TCP 1323 scale factor and changes it on the fly, disregarding
this setting. Additional testing may be required to determine it's
effect if auto-tuning is turned off. Setting it to 1 is best for broadband connections.
NetDMA (TCPA)
NetDMA
enables support for advanced direct memory access. In essence, it
provides the ability to more efficiently move network data by minimizing
CPU usage. NetDMA frees the CPU from handling memory data transfers
between network card data buffers and application buffers by using a DMA
engine.
Under Windows 7, NetDMA can be set directly using the netsh interface (not available under Vista):
netsh int tcp set global netdma=enabled
Under Vista/2008/7, you can set NetDMA/TCPA using the following Registry parameter:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
EnableTCPA=1 (DWORD, not in registry by default. Set to 1 to enable, 0 to disable NetDMA)
Recommended
setting is 1 (if not using Chimney Offload), zero otherwise. A new
DWORD value may need to be created if not already present in the
registry.
For NetDMA to work, it must be enabled in BIOS,
your CPU must support Intel I/O Acceleration Technology (I/OAT), and it
does not work together with Chimney Offload. More info available -here-
Checksum Offloading (DisableTaskOffload)
This NDIS 5 setting allows for reducing CPU load by offloading some tasks required to maintain the TCP/IP stack to the network card. Theoretically, Widnows should automatically detect capable network hardware.
The tasks offloaded are as follows:
- TCP/IP checksum calculation - each packet sent includes a verification checksum.
- TCP/IP segmentation - also known as "TCP Large Send" where Windows sends a large amount of data to the network card, and the NIC is then responsible for dividing it according to the network MTU. Experimental feature, not enabled by default
- IPSec Encryption cyphers and message digests - provides encryption of packets at the hardware level.
To change the checksum offloading setting in the Windows Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
DisableTaskOffload=0 (DWORD value, default: not set, recommended: 0=enable offload, 1=disable offload)
Also see: MS KB 888750, MS KB 904946, MS KB 936702
DefaultTTL
TTL can be safely left alone in many cases. It is a limit to the time and number of hops/routers a packet
will travel before being discarded. A number that's too small risks
packets being discarded before reaching their destination. A number
that's too large (over 128) will cause delay in when lost IP packets are
discarded.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
DefaultTTL=64 (DWORD, set to a decimal value between 32 and 128. Recommended: 64)
TcpMaxDataRetransmissions
Determines
how many times unacknowledged data (non-connect segment) is
retransmitted before TCP aborts the connection. The retransmission
timeout is doubled with each successive retransmission on a connection.
It is reset when responses resume.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
TCPMaxDataRetransmissions=7 (DWORD, recommended: between 3 and 10, not present in registry by default)
Note: When not present in the registry, the default behavior is 255 retransmissions (5 in documentation).
SynAttackProtect
This
undocumented for Windows 7 setting provides protection against SYN
denial of service (DoS) attacks. When enabled, connections timeout
sooner if SYN attack is detected. When set at 1,
TCPMaxDataRetransmissions can be lowered further.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
SynAttackProtect=1 (DWORD, recommended: 1, not present in registry by default)
Note: MSDN suggests a value of 2 for Windows 2k - http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa302363.aspx
EnableConnectionRateLimiting
This
parameter sets (or disables) the half-open TCP connection limit in
Windows 7, Vista (SP2), Server 2008, or later. Some Microsoft OSes, such
as, Vista before SP2, and 2008 Server before SP2, may limit the number
of half-open TCP connections to 10. Limiting the half-open
(incomplete) TCP connections per second may lead to log errors which
read as follows: "Event ID 4226: TCP/IP has reached the security limit imposed on the number of concurrent TCP connect attempts". It may cause P2P
and other programs that open a large number of connections to be
somewhat limited in ramping up their transfers. It is recommended to
remove this limitation. Just check the below key and make sure it is
either not present, or set to zero. Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008
SP2 or later should not have to make any changes.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
EnableConnectionRateLimiting=0 (DWORD, recommended: 0, or delete key)
Network Throttling Index
By
default, Windows Vista/7 implements a network throttling mechanism to
restrict the processing of non-multimedia network traffic to 10 packets
per millisecond (a bit over 100 Mbits/second). The idea behind such
throttling is that processing of network packets can be a
resource-intensive task, and it may need to be throttled to give
prioritized CPU access to multimedia programs. In some cases, such as
Gigabit networks and some online games, for example, it may be
benefitial to turn off such throttling all together.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Multimedia\SystemProfile
NetworkThrottlingIndex=ffffffff (DWORD, default: 10 hex, recommended: 10 hex for media sharing, ffffffff for gaming and max throughput, valid range: 1 through 70 decimal or ffffffff to completely disable throttling)
It is only recommended to change this setting in saturated Gigabit LAN
environments, where you do not want to give priority to multimedia
playback. Reportedly, disabling throttling by using ffffffff can also
help reduce ping spikes in some online games.
Notes:
Setting is available in Windows 7, Vista (SP1), 2008 Server. Default
value is 10 under Windows 7, similar behavior if the setting is not
present in the Registry.
Games that may be affected by this throttling: Source Engine games (TF2, Left 4 Dead, CS:S), HoN, CoD, Overlord series.
Reference: MSKB 948066
Set DNS and Hosts Priority
As with previous versions of Windows, one can improve DNS
and hostname resolution by increasing the priority of of related
services, while keeping their order. This is explained in more defail in
our Host Resolution article. Lower numbers mean higher process priority. The corresponding registry settings in Vista are as follows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\ServiceProvider
LocalPriority=4 (DWORD, recommended: 4, default: 499) - local names cache
HostsPriority=5 (DWORD, recommended: 5, default: 500) - the HOSTS file
DnsPriority=6 (DWORD, recommended: 6, default: 2000) - DNS
NetbtPriority=7 (DWORD, recommended: 7, default: 2001) - NetBT name resolution, including WINS
TcpTimedWaitDelay (port allocation)
Short lived (ephemeral) TCP/IP
ports above 1024 are allocated as needed by the OS. The default
Vista values have improved from previous Windows versions, and are
usually sufficient under normal load. However, in some instances under
heavy load it it may be necessary to adjust the settings below to tweak
the availability of user ports requested by an application.
If the default limits are exceeded under heavy loads, the following error may be observed: "address in use: connect exception".
By default under Vista (when the values are not presend in the
registry), the OS can allocate up to 16384 ephemeral ports above
port 1024, and the OS waits for 120 seconds before reclaiming ports
after an application closes the TCP connection. This is a considerable
improvement over older Windows versions. However, if necessary, the
following registry values can be added/edited:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
MaxUserPort=65534
(DWORD, not in the registry by default. Recommended: leave at
default, or use a number above 16384 up to 65534 decimal as necessary) -
maximum number of ports to use. 1024 is automatically subtracted from
entered value to allow for reserved ports under 1024.
TcpTimedWaitDelay=30
(DWORD, not present or 0xffffffff in registry by default. Recommended:
30 decimal, denoting 30 seconds) - time to wait before reclaiming ports,
in seconds. Default time before reclaiming ports, if value is at
0xffffffff or not present in the registry is 120 seconds. Just reducing
the delay is often sufficient without changing MaxUserPort, as it allows
for reusing ports more efficiently.
Ephemeral ports can be checked and changed using netsh as well.
To query the current values, in command prompt, type:
netsh int ipv4 show dynamicportrange tcp (for UDP, use the same command, replacing only "tcp" with "udp" at the end)
To set both the starting, and max user port using netsh, in elevated command prompt run:
netsh int ipv4 set dynamicportrange protocol=tcp start=1025 num=64511 (start=NNN denoting the starting port, and num=NNN denoting the number of ports)
Notes:
By default, dynamic ports are allocated between ports 49152 and 65535 (for a total of 16384 ephemeral ports).Using
netsh allows to set both the starting port and port range. Editing the
Registry allows for setting the port range, and the starting port is
fixed at 1025. Deleting the MaxUserPort registry entry (or setting it to
a value outside the allowed range) causes the OS to revert to using the
default values.Some system processes can install port
filters to block certain port ranges. If ephemeral ports run into these
filtered port ranges, TCP/IP applications will be unable to bind to any ports.
See also: TechNet article, MSKB 328476, MSKB 319502
QoS Reserved Bandwidth
As with Windows XP, nework adapters have a "QoS Packet Scheduler" enabled by default, which reserves 20% of bandwidth by default for QoS applications that request priority traffic. Note this only has effect in the presence of running QoS
applications that request priority traffic. Registry value is
undocumented for the Vista version of Windows. To customize this
setting, in the Windows Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Psched
NonBestEffortLimit=0
(DWORD, not present in the registry by default. Recommended: 0 ,
possible values between 0 and 100) - indicates the percentage value of
reserved bandwidth for QoS applications. Set to 0 to disable.
Notes: This tweak applies only to Windows versions that have Qos Packet Scheduler enabled. It will ONLY have effect in the presense of running QoS applications.
Network Memory Allocation (Event ID 2017 error)
When
using Windows Vista/7 to serve many/large files over the local network,
it is possible to sometimes run into memory allocation errors related
to the Windows share. This can happen with Linux, Mac, or Windows XP clients. When this happens, you can usually see the following error in the Event Viewer System log:
Source: srv
Event ID: 2017
Level: Error
The
server was unable to allocate from the system nonpaged pool because the
server reached the configured limit for nonpaged pool allocations.
It
is also possible to get an error indicating that: "Not enough server
storage is available to process this command". To avoid those errors,
you need to change the way Windows allocates memory for network services
and file sharing. The below settings optimze the machine as a file
server so it would allocate resources accordingly. There are two related
registry settings:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management
LargeSystemCache=1 (DWORD, default value: 0, recommended value: 1)
A
value of zero above establishes a cache of ~8 MB, a value of 1 allows
the cache to expand to physical memory minus 4 MB, if needed.
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Size=3 (DWORD, default value: 1, recommended value: 3)
Size=1 minimizes used memory
Size=2 balance used memory
Size=3 optimal setting for file sharing and network applications
Note:
Even though this tweak is from older Windows server OSes, it works on
workstation versions, as well as Windows Vista and 7 (32 and 64 bit).
Gaming Tweak - Disable Nagle's algorithm
The
tweak below allows for tweaking or disabling Nagle's alogrithm.
Disabling "nagling" allows for very small packets to be transferred
immediately without delay. Note that disabling Nagle's algorithm is only
recommended for some games, and it may have negative impact on file
transfers/throughput. The dafault state (Nagling enabled) improves
performance by allowing several small packets to be combined together
into a single, larger packet for more efficient transmission. While this improves overall performance and reduces TCP/IP
overhead, it may briefly delay transmission of smaller packets. Keep in
mind that disabling Nagle's algorithm may have some negative effect on
file transfers, and can only help reduce delay in some games. To
implement this tweak, in the registry editor (Start>Run>regedit) find:
This setting configures the maximum number of outstanding ACKs in Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\{NIC-id}
There will be multiple NIC interfaces listed there, for example: {1660430C-B14A-4AC2-8F83-B653E83E8297}. Find the correct one with your IP address listed. Under this {NIC-id} key, create a new DWORD value:
TcpAckFrequency=1 (DWORD value, 1=disable, 2=default, 2-n=send ACKs if outstanding ACKs before timed interval. Setting not present by default).
For gaming performance, recommended is 1 (disable). For pure throughput and data streaming, you can experiment with values over 2. If you try larger values, just make sure TcpAckFrequency*MTU is less than RWIN, since the sender may stop sending data if RWIN fills witout acknowledgement.
Also, find the following key (if present):
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSMQ\Parameters
Add a new DWORD value:
TCPNoDelay=1 (DWORD value, 0 to enable Nagle's algorithm, 1 to disable, not present by default)
To configure the ACK interval timeout (only has effect if nagling is enabled), find the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\{NIC-id}
TcpDelAckTicks=0
(DWORD value, default=2, 0=disable nagling, 1-6=100-600 ms). Note you
can also set this to 1 to reduce the nagle effect from the default of
200ms without disabling it.
Notes:
Reportedly, the above gaming tweak (disabling nagle's algorithm) can reduce WoW (World of Warcraft) latency by almost half!XP/2003 needs hotfix or SP2 for it to work (MS KB 815230)
Vista needs hotfix or SP1 for it to work (MS KB 935458)
See also: NetworkThrottlingIndex setting above
SG TCP Optimizer (version 3.x)
The
TCP Optimizer version 3.x allows for easy application of the above
settings under all current Windows versions. This free software provides
an intuitive interface for tunning your internet connection, backing
up/restoring to the Windows defaults, etc. There is no installation
required, you can just save it to the desktop, right-click > run as
administrator and choose your settings. More detailed information about
all available options is provided in the online documentation, answers to frequently asked questions are available in the Optimizer FAQ, and personalized help is available through our broadband tweaking forum.
SG TCP Optimizer download
For user convenience, we also provide a quick way to apply all optimal values as recommended above using our SG Vista TCP/IP Patch.
It allows for tweaking all the above netsh settings and registry values
in one simple step (with the exception of the "gaming tweak" section).
The patch
also provides for easily reverting the settings to their Windows
default values. To apply, save to your desktop and run as administrator
(right-click -> run as administrator). Click Y when prompted to apply
settings.
Note: If for some reason Windows renames the file and
adds .txt extension to it, you may have to manually rename it back to
have a .cmd (or .bat) extension before running it as administrator.
See Also
Windows Vista tcpip.sys connection limit patch for Event ID 4226 - removing the limit on half-open TCP connections.
|












